What is Hearing Protection?
Hearing protection is personal protective equipment (PPE) for reducing noise exposure. Hearing protection devices reduce the noise energy that can cause damage to the inner ear. Earmuffs and earplugs are the most common types hearing protectors for reducing noise exposure.
-
Noise-induced Hearing Loss
-
When is Hearing Protection Required?
-
Types of Hearing Protectors
-
Choosing the Right Hearing Protection

Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Noise-induced hearing damage continues to be the most common occupational disease among working-age people. It is up to three times more common than the second most common occupational disease, irritant contact dermatitis.
Occupational noise-induced hearing damage is caused most commonly by the manufacturing of metal products, specialized construction work, military duties, public safety professionals, the manufacturing of other machines and equipment, and building construction.
Workplaces are aware of the fact that hearing protection designed for professional use can prevent noise-induced hearing impairments and damage...so why does it continue to be the most common occupational disease?
Read more: Noise-Induced Hearing loss the most common occupational disease →
Read more: Hearing Protection for Public Safety Officers Bigger Need than Realized →
Problems in misuse of hearing protectors or attitudes
People forget to use or misuse the equipment. Workers may instinctively take off their hearing protection when they stop to talk to someone or answer the phone.
Hoods and headgear are occasionally left between the earmuffs and the wearer’s skin. Sometimes, other protective equipment worn on the face can prevent the earmuffs from forming a proper seal also causing leaks.
There is also plenty of room for improvement in people’s attitudes. Sentences like “I’ll just quickly pop in there” or “it’s not that loud” are heard too often at workplaces. Noise-induced damage is not taken seriously enough, and people do not understand how sensitive the hearing organs are.
Noise-induced hearing damage cannot be cured, but it can be prevented by protecting hearing with hearing protection in excessively noisy environments.
Subcribe to our blog
Be among the first of your peers to hear about the new products and solutions from Savox.
When is hearing protection required?
Hearing protectors are required to prevent noise induced hearing loss caused by excessive noise. Excessive noise and the need for hearing protection is determined by the decibel level in a specific environment.
Here are examples of common noisy environments:
-
Airport
-
Industrial factory
-
Construction site.
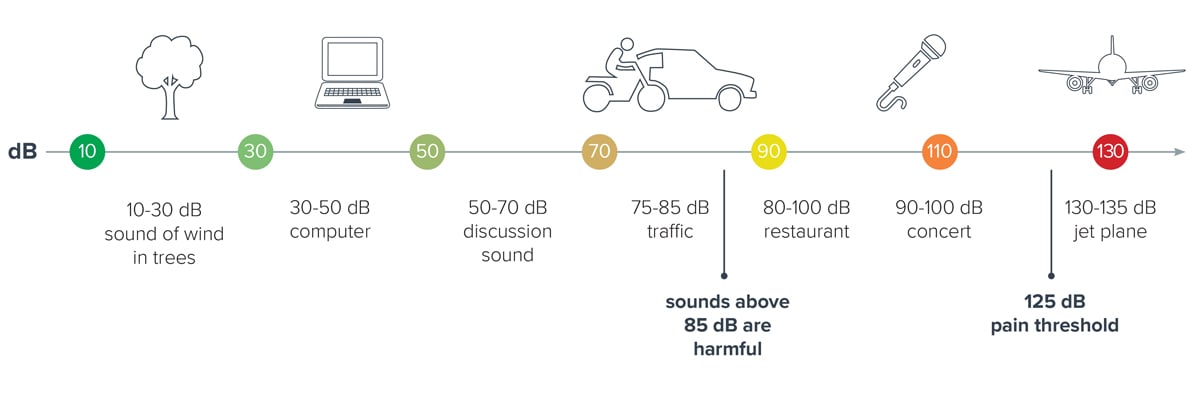
At what decibel is hearing protection required?
Decibels (dB) is an important measurement to understand when discussing hearing protection. Normal conversation is about 60 dB, a lawn mower is about 90 dB, and a loud rock concert is about 120 dB. In general, sounds above 85 are harmful, depending on how long and how often you are exposed to them and whether you wear hearing protection. When working above 80 dB employer must provide CE-marked and EN352 tested hearing protectors to employees.
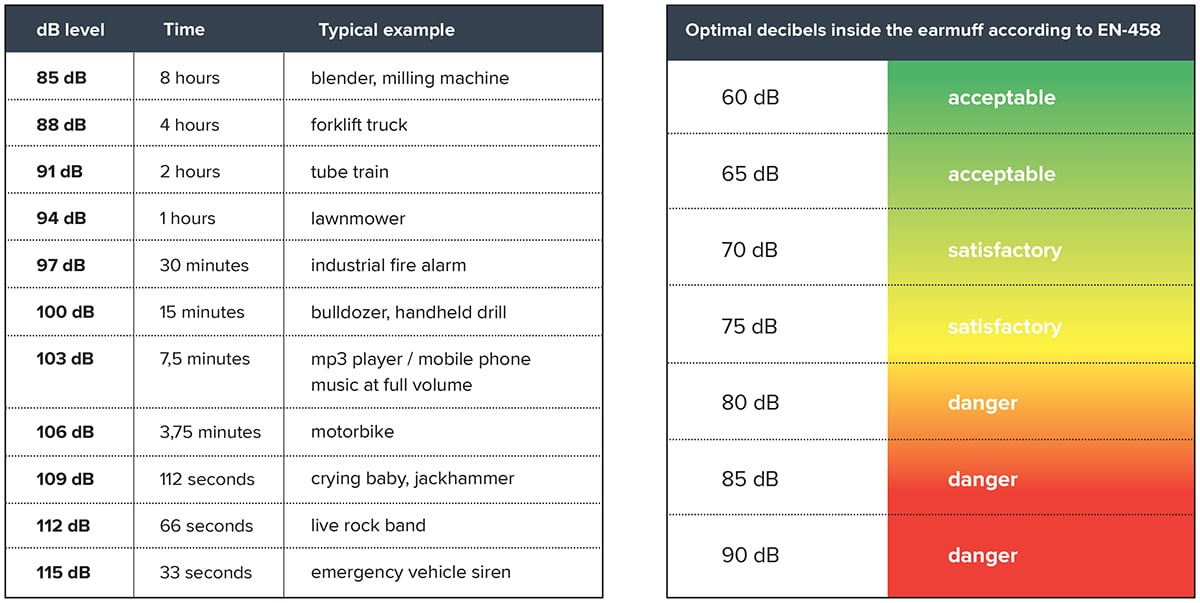
Noise Reduction Values
Understanding noise reduction values: SNR, H, M and L -Values
Every hearing protector is required to have noise reduction values. These values are used in Europe: SNR value The SNR (Single Number Rating) indicates an insulation value averaged over the relevant frequencies. An SNR value of 35 dB, for example, absorbs 100 dB and reduces it to 65 dB. HML values The HML values indicate how high sound reduction there is in three frequency ranges, H (high), M (middle) and L (low) is.
These frequencies are:
H (High) between 2000 and 8000 Hz
M (Middle) between 1000 and 2000 Hz
L (Low) between 63 and 1000 Hz
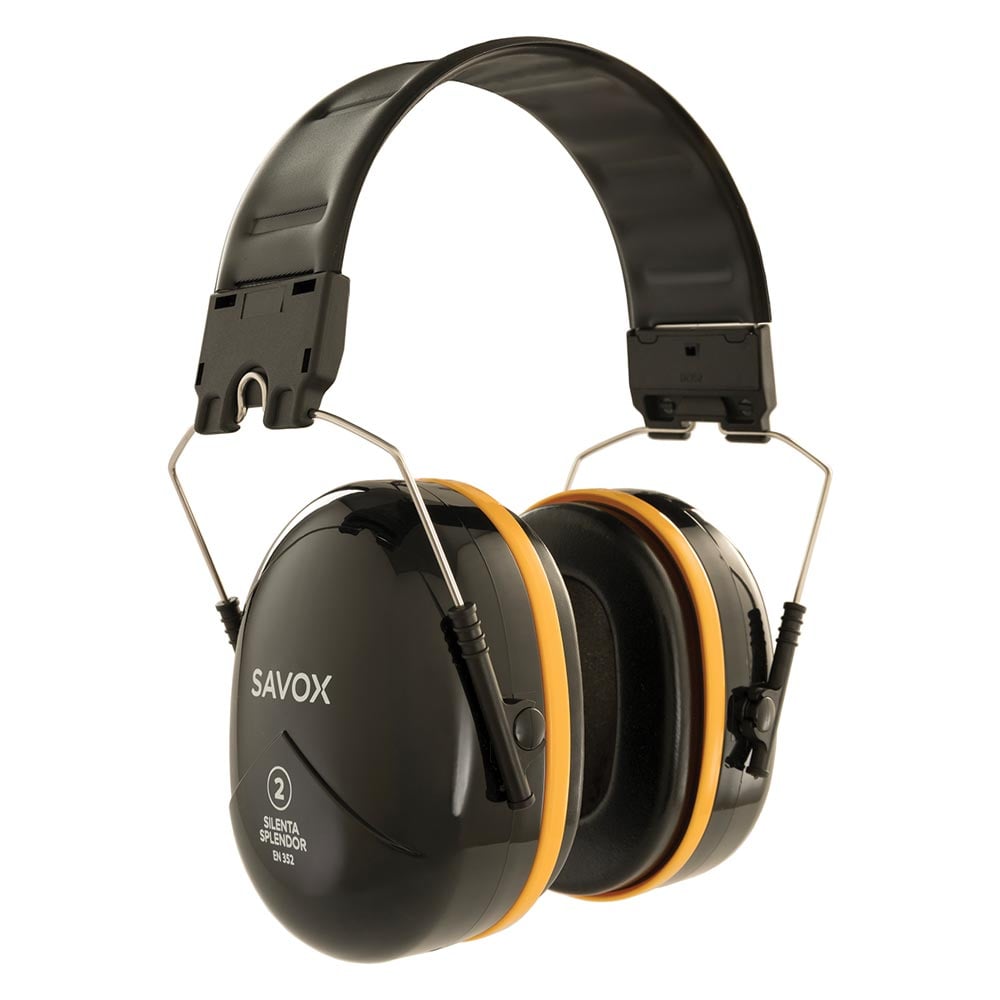
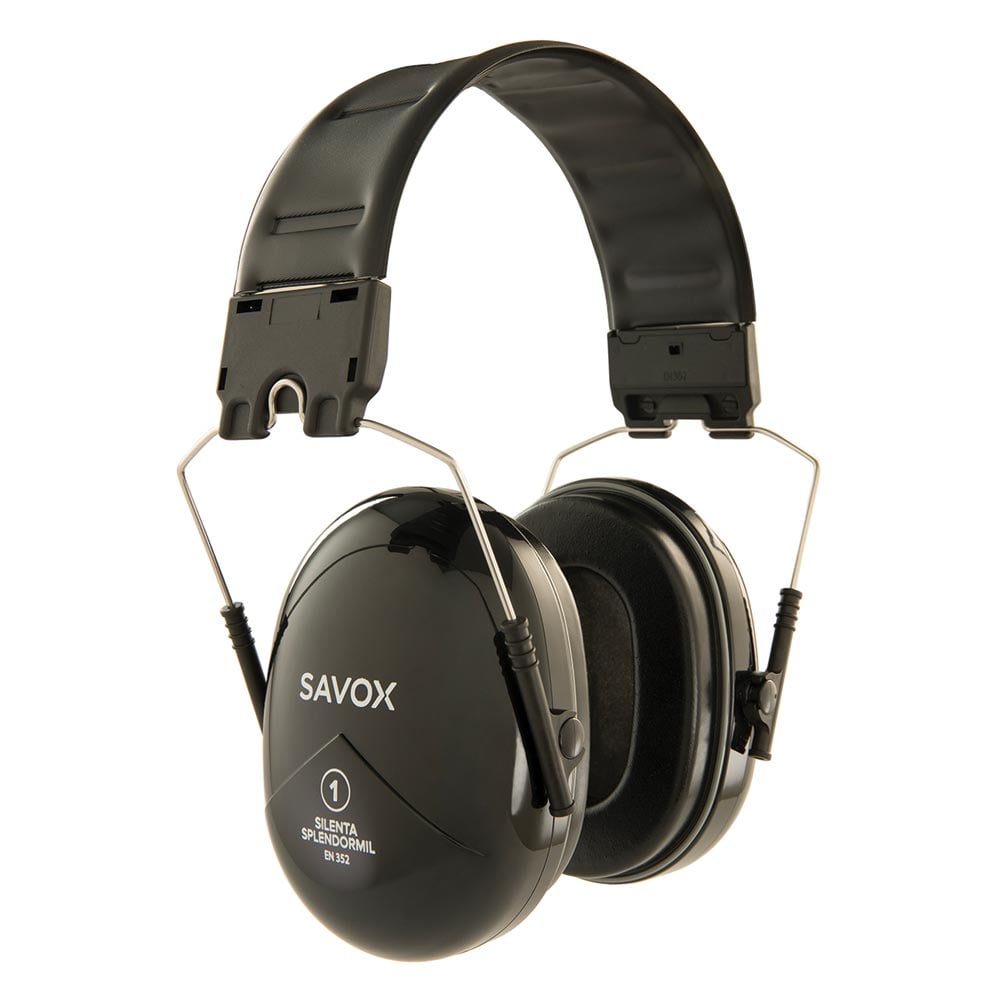
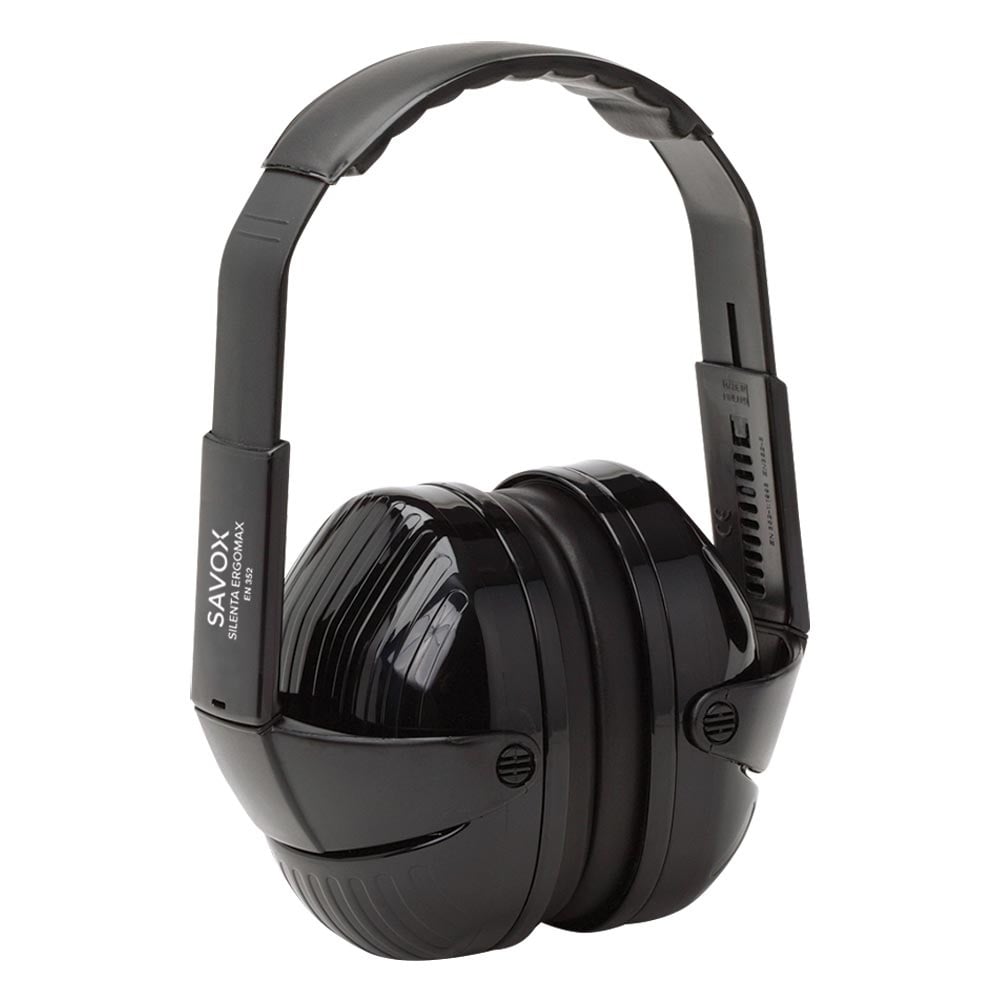
Types of Hearing Protectors
Hearing protection devices reduce the noise energy reaching and causing damage to the inner ear. Earmuffs and earplugs are the most common types of personal protective equipment (PPE) for reducing noise exposure.
Earplugs
Earplugs are inserted into the ear canal. Earplugs are convenient in size and portability; however, they do come with hygiene issues. Earplugs also rarely provide enough protection against extreme noises on their own.
Earmuffs
Earmuffs are a very common type of hearing protection PPE. Earmuffs are favored by professionals, because they offer great noise attenuation and durability. Earmuffs can be categorized into two types, which will be explained in more detail after the chart:
- Passive hearing protection
- Communication/ electronic hearing protection
| Earplugs | Earmuffs |
Advantages:
|
Advantages:
|
|
Disadvantages: |
Disadvantages: |
|
|
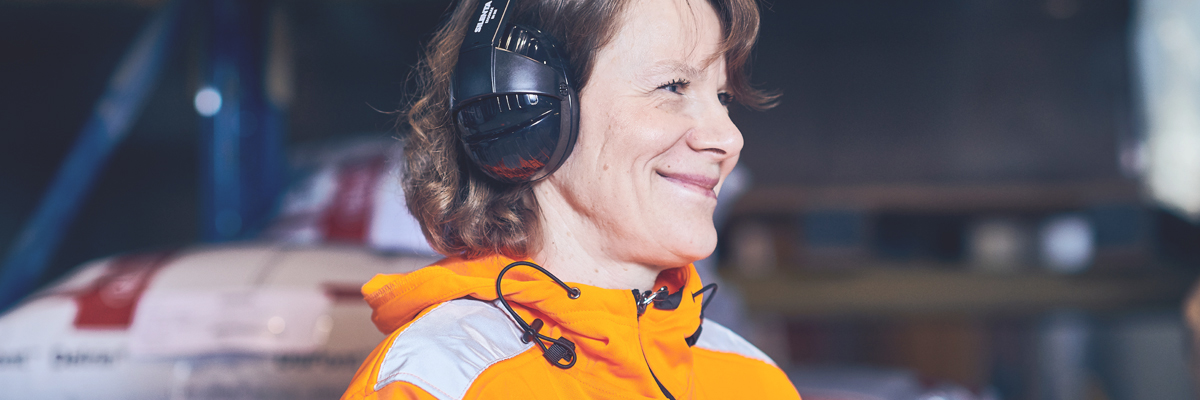

Passive Hearing Protection
Passive hearing protectors are the most practical and cost-efficient alternative when there’s no communication requirements and the attenuation of the noises in the surroundings does not generate a hazard risk. Key features for these headsets are the level of protection and user comfort, and compatibility to other safety wear such as helmets.
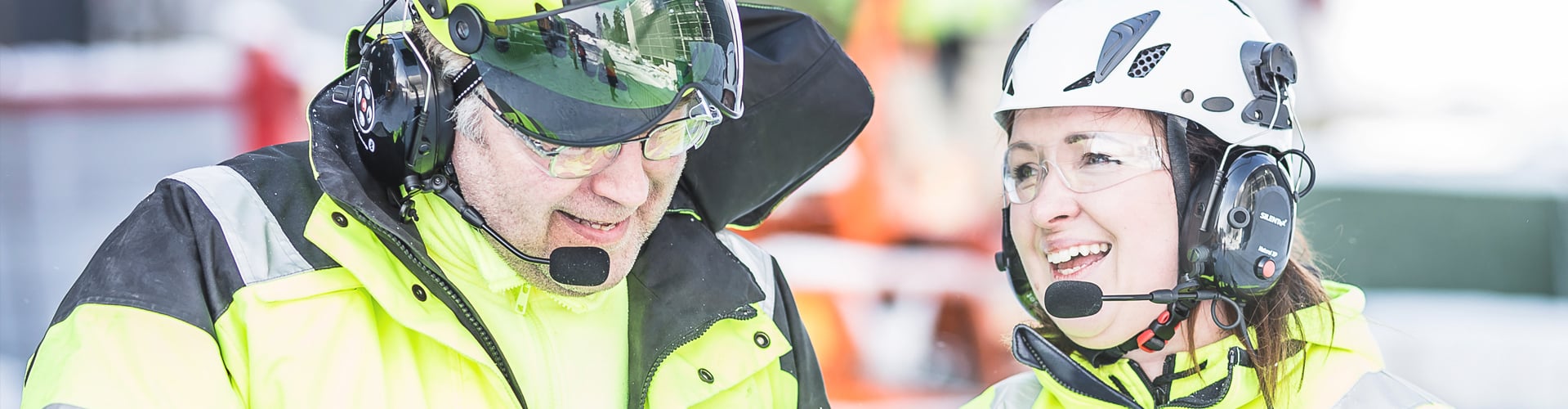

Electronic Hearing Protection
Electronic earmuffs, also known as communication hearing protectors, are an important safety factor in several work environments. Electronic hearing protectors offer the ability to remain aware of the environment and possible alarms. The user can continue to work efficiently communicating with the colleagues with a phone or radiophone without leaving the noisy area. Fine-tuned details and functions also increase the product’s comfort.
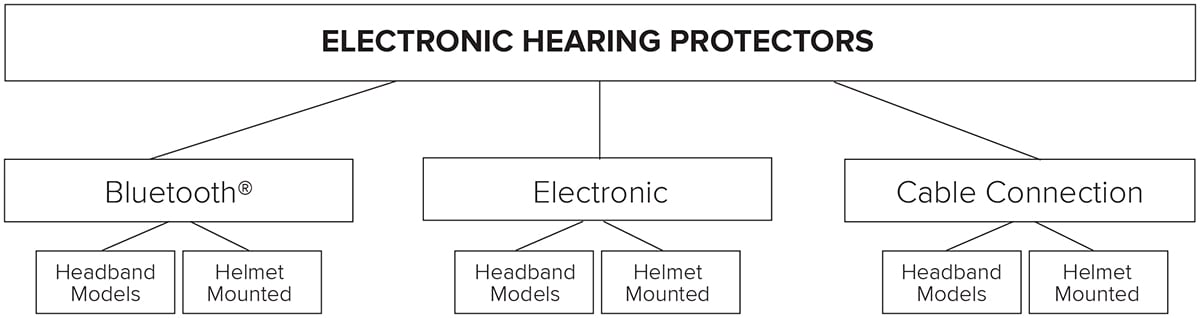
Electronic hearing protectors can be divided into three categories:
- Bluetooth® Earmuffs
- Electronic Earmuffs
- Earmuffs with Cable Connection.
Hearing Protection with Wireless Bluetooth Technology
Wireless hearing protection headset for environments with high noise-levels. The headset offers wireless connection to Bluetooth® enabled devices such as mobile phones and communication radios.
Bluetooth with Active Hearing Headset
Active ambient sound reproduction protects hearing from harmful noise, while warning signals, speech, instructions, and other signals in lower levels of noise can be heard.- Improves safety by not isolating the user from the surroundings
- Maximum sound pressure level from earphones is limited to 82 dB
Cable Connection Hearing Protection
Hearing protection headset with direct connection to communication radio.
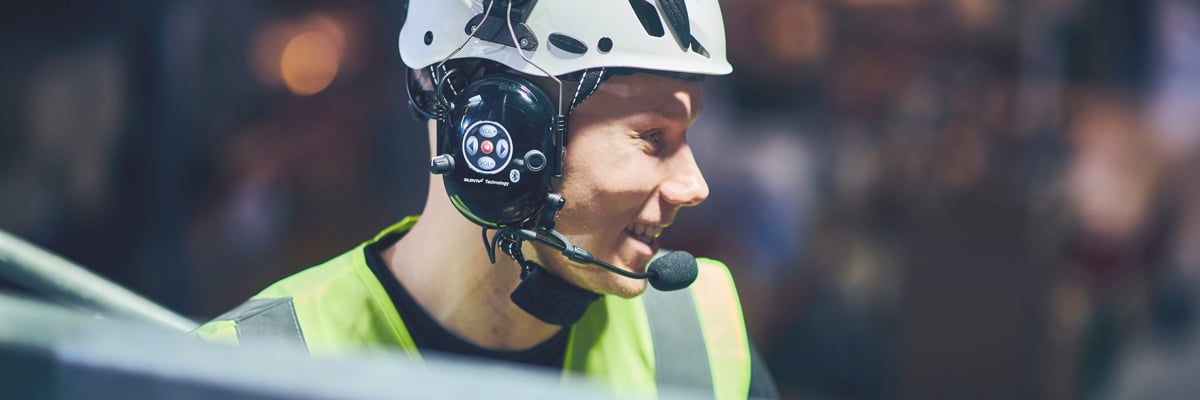

How to Determine the Correct Hearing Protector
Choosing the right hearing protection can be a daunting task. However, by understanding technical functions, attenuation values and industry requirements, it will be simple.
Choosing the Right Hearing Protection Checklist
- Correct and suitable features for the job/ operation
- Provides adequate protection and noise attenuation - Check the manufacturer's information and instructions.
- Compatible with other required personal protective equipment, or communication devices.
- Comfortable enough to be worn long periods of time.
- Appropriate for the temperature and humidity in the workplace.
- Able to provide adequate communication and audibility needs (e.g., the ability to hear alarms or warning sounds).
- Has the option to change earmuffs for hygiene purposes
Maintenance and storing hearing protectors
Hearing Protection is personal protective equipment, meaning equipment is designed for personal use.
To minimize the risk of contamination it’s recommendable to clean the hearing protector regularly and to replace the earmuff cushions at least every 6 months in order to guarantee the best performance and user experience.
Earmuffs and in particular cushions may deteriorate with use and should be examined at frequent intervals for example for cracking and leakage. Replace the cushions as necessary, at least every 6 months. Pull off the old cushions and press the new ones carefully and firmly on all areas into their proper place on the ear-cups. The ear-cup foam liners should also be replaced when required. The headband should not be flexed or adjusted unnecessarily, as the correct pressure is an important factor maintaining the attenuation afforded by these earmuffs.










